LED light bulbs are considered to be more energy-efficient, bright and cost-effective compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Despite technical advances, incandescent bulbs are still superior when it comes to offering homey quality of light. However, some major pitfalls are that they don’t last longer and also waste lot of energy in form of heat.
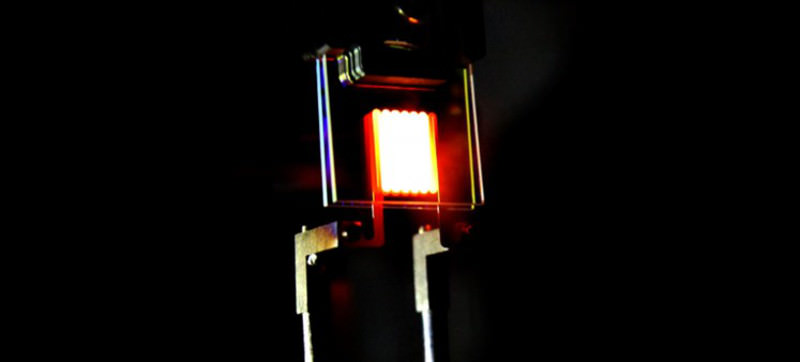
Not anymore, as MIT researchers have developed a new invention to make incandescent bulbs more efficient than LEDs. Well, they have created new incandescent bulb that is embedded with nano-scale mirrors to eliminate wastage of infrared emissions. These mirrors are used to bounce wasted heat energy back at the filament, allowing visible light to spread more.
MIT’s design uses photonic crystals for allowing light in the visible spectrum to pass straight through and reflect infrared back towards the filament. The reflected infrared radiations are further absorbed and re-emitted once again in form of visible light. This back-and-forth processing continues to help improve efficiency of the light bulb.
The process sounds simple, but it was not easy to develop. Firstly, the research team had to make the photonic crystals, which are able to transmit visible light and reflect infrared radiations. After that, they layered about 90 nano-scale layers of tantalum oxide and silicon dioxide for creating sufficient light reflection. Filament is also redesigned for creating a larger surface area to absorb the reflected radiation.
Final design is a thin, folded ribbon of tungsten. MIT’s new incandescent light bulbs are able to convert 6.6-percent of the electricity into light. So, it’s going to be three times better than a regular incandescent bulbs, and of course better than LED bulbs that are available on the market.
Via: FastCoDesign
Follow Homecrux on Google News!




